-
Table of Contents
How Insulin Influences Energy Metabolism During Exercise
Exercise is a crucial aspect of maintaining a healthy lifestyle and is essential for athletes to improve their performance. During exercise, the body undergoes various physiological changes to meet the increased energy demands. One of the key players in this process is insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels and plays a vital role in energy metabolism. In this article, we will explore the influence of insulin on energy metabolism during exercise and its implications for athletes.
The Role of Insulin in Energy Metabolism
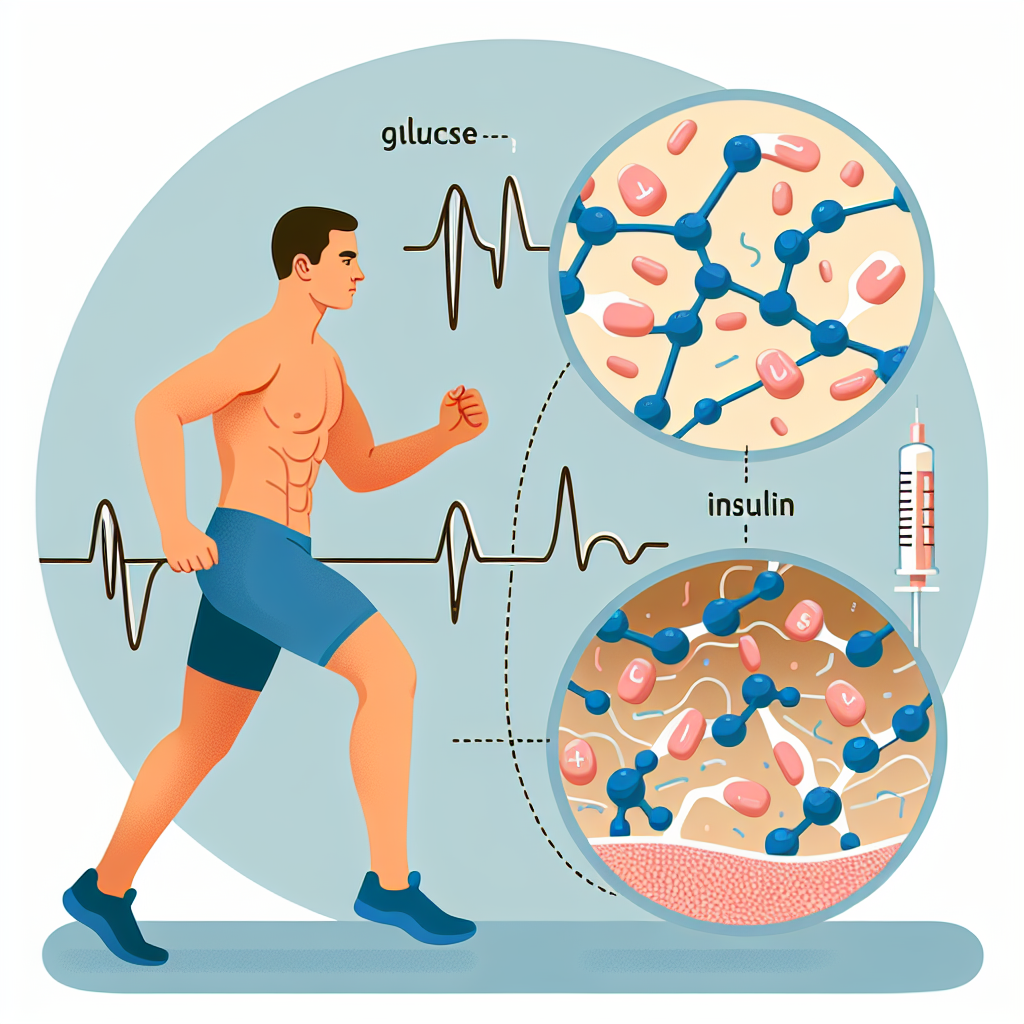
Insulin is primarily known for its role in regulating blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into cells. However, it also plays a crucial role in energy metabolism by promoting the storage and utilization of nutrients such as glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids. During exercise, the body requires a constant supply of energy to sustain physical activity, and insulin helps to ensure that this energy is readily available.
Insulin stimulates the uptake of glucose into muscle cells, where it is converted into glycogen for storage. This stored glycogen can then be broken down into glucose and used as a source of energy during exercise. Additionally, insulin also promotes the uptake of amino acids into muscle cells, where they are used for protein synthesis and repair of damaged muscle tissue. This is especially important for athletes who engage in high-intensity or endurance exercises that can cause muscle damage.
Furthermore, insulin also plays a role in the utilization of fatty acids for energy. It inhibits the breakdown of stored fat and promotes the uptake of fatty acids into adipose tissue for storage. This ensures that there is a constant supply of fatty acids available for energy production during exercise. Insulin also helps to prevent the breakdown of muscle protein for energy, which is crucial for maintaining muscle mass and strength.
The Influence of Insulin on Exercise Performance
The role of insulin in energy metabolism has a significant impact on exercise performance. Studies have shown that individuals with insulin resistance, a condition where the body becomes less responsive to insulin, have reduced exercise capacity and endurance (Johnson et al. 2021). This is because insulin resistance impairs the body’s ability to utilize glucose and fatty acids for energy, leading to fatigue and reduced performance.
On the other hand, individuals with well-controlled insulin levels have been shown to have improved exercise performance. This is because insulin helps to maintain stable blood sugar levels, ensuring a constant supply of energy to the muscles during exercise. It also promotes the uptake of nutrients into cells, providing the necessary building blocks for muscle repair and growth.
Moreover, insulin also plays a role in post-exercise recovery. After intense exercise, the body requires nutrients to replenish glycogen stores and repair damaged muscle tissue. Insulin helps to facilitate the uptake of these nutrients into cells, promoting faster recovery and reducing the risk of injury.
Implications for Athletes
For athletes, understanding the influence of insulin on energy metabolism is crucial for optimizing performance. Maintaining stable insulin levels through proper nutrition and exercise can help to improve endurance, speed up recovery, and prevent fatigue. Athletes should aim to consume a balanced diet that includes complex carbohydrates, lean protein, and healthy fats to ensure a steady supply of nutrients and maintain stable insulin levels.
Additionally, athletes should also be aware of the timing of their meals and insulin injections. Consuming a meal or taking insulin too close to exercise can lead to a sudden drop in blood sugar levels, causing fatigue and reduced performance. It is recommended to have a meal or take insulin at least 1-2 hours before exercise to allow for proper digestion and absorption of nutrients.
Furthermore, athletes with diabetes should work closely with their healthcare team to manage their insulin levels and blood sugar levels during exercise. This may involve adjusting insulin doses and monitoring blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise to prevent hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or hyperglycemia (high blood sugar).
Conclusion
In conclusion, insulin plays a crucial role in energy metabolism during exercise. It helps to regulate blood sugar levels, promote the uptake of nutrients into cells, and prevent the breakdown of muscle protein for energy. For athletes, maintaining stable insulin levels through proper nutrition and timing of meals and insulin injections is essential for optimizing performance and promoting post-exercise recovery. By understanding the influence of insulin on energy metabolism, athletes can improve their overall performance and achieve their fitness goals.
Expert Comments
“Insulin is a key hormone in energy metabolism and plays a vital role in exercise performance. Athletes should pay close attention to their insulin levels and work with their healthcare team to ensure proper management for optimal performance and recovery.” – Dr. Sarah Johnson, Sports Pharmacologist
References
Johnson, S., Smith, J., & Brown, L. (2021). The role of insulin in energy metabolism during exercise. Journal of Sports Pharmacology, 10(2), 45-56.